Research Topics
Information Retrieval, Natural Language Processing, Digital Libraries
(1) User-Centric Information Retrieval, Recommender Systems

Web Pages
Web search engines help users find useful information on
the World Wide Web (WWW). However, when different users submit the same query,
typical search engines return the same result regardless of
who submitted the query. Generally, each user has different information needs
for his/her query. Therefore, we have developed several methods for adapting
search results according to each user's information need.

Scholarly Papers
Much of the world's new knowledge is now largely
captured in digital form and archived within a digital library system.
However, these trends lead to information overload, where users find
an overwhelmingly large number of publications that match their search queries
but are largely irrelevant to their latent information needs. Therefore,
we develop methods for recommending scholarly papers relevant to
each researcher's information needs. Furthermore, among researchers,
junior researhers need to broaden their range of
research interests to acquire knowledge, while senior researchers
seek to apply their knowledge towards other areas to lead interdisciplinary
research. Therefore, we have also developed methods for recommending scholarly papers
that are serendipitous to each researcher's research interests.

Mobile Apps
Users can access a substantial number of apps via App Stores.
Furthermore, the selection available in app stores is growing rapidly as new apps are
approved and released daily. While this growth has provided users with a myriad of
unique and useful apps, the sheer number of choices also makes it more difficult
for users to find apps that are relevant to their interests. To solve this problem,
we have proposed recommendation systems for mobile apps that employ Twitter information
which can precede formal user ratings in app stores, and version information
which is specific to mobile apps. In this topic, we also have developed
a recommendation system for serendipitous apps using a graph-based approach.
[Selected publications]
Web Pages
- Kazunari Sugiyama: ``Adaptive Web Search Based on a Word-Based Collaborative
Filtering That Overcomes Data Sparsity'' (in Japanese), The Japanese Society for Artificial
Intelligence (JSAI), Technical Report SIG-FPAI-A702-02, pp.7-12,
Kanagawa, Japan, November 2007. [pdf]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Kenji Hatano, Masatoshi Yoshikawa and Shunsuke Uemura: ``Adaptive Web Search Based on User Profile Constructed without Any Effort from Users'' (in Japanese), The Transactions of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE), Vol.J87-D-I, No.11, pp.975-990, November 2004. [pdf]
Scholarly Papers
- Kazunari Sugiyama and Min-Yen Kan: ``A Comprehensive Evaluation of Scholarly Paper Recommendation Using Potential Citation Papers,'' International Journal on Digital Libraries, Springer, Vol. 16, Issue 2, pp.91-109, June 2015.
- Kazunari Sugiyama and Min-Yen Kan: ``Towards Higher Relevance and Serendipity in Scholarly Paper Recommendation'' with Martin Vesely as coordinator,
ACM SIGWEB Newsletter, Winter, Article No. 4, 2015. [pdf]
Mobile Apps
- Jovian Lin, Kazunari Sugiyama, Min-Yen Kan, and Tat-Seng Chua:
``Scrutinizing Mobile App Recommendation: Identifying Important App-related Indicators,''
The 12th Asia Information Retrieval Societies Conference (AIRS 2016),
Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Springer-Verlag, Vol.9994, pp.197-211,
Beijing, China, November 30-December 2, 2016. [pdf]
(2) Methods for Characterizing Documents

In information retrieval systems based on the vector space model,
and researches such as document classification or clustering,
the TF-IDF scheme is widely used to characterize documents. However,
the TF-IDF scheme does not always assign appropriate weights
(i.e., higher weights) to terms that characterize a document. In addition,
in the case of documents with hyperlink structures such as Web pages,
it is necessary to develop a technique for representing the contents of
Web pages more accurately by exploiting the contents of their hyperlinked
neighboring pages. Therefore, I have developed:
(a) methods for characterize documents using information
about terms such as which position in a sentence the term appears,
which paragraph in the document the term appears, or the term begins capital
letter or not,
(b) methods for refining the TF-IDF scheme for a target Web page
by using the contents of its hyperlinked neighboring pages.
[Selected publications]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Kenji Hatano, Masatoshi Yoshikawa and Shunsuke Uemura: ``Improvement in TF-IDF Scheme for Web Pages based on the Contents of Their Hyperlinked Neighboring Pages,'' Systems and Computers in Japan, Vol.36, No.14, pp.56-68, February 2005. [pdf]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Kenji Hatano, Masatoshi Yoshikawa and Shunsuke Uemura: ``Improvement in TF-IDF Scheme for Web Pages based on the Contents of their Hyperlinked Neighboring Pages'' (in Japanese), The Transactions of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE), Vol.J87-D-I, No.2, pp.113-125, Feburary 2004. [pdf]
(3) Personal Name Disambiguation in Web Search Results
Personal names are often submitted to search engine as query keywords.
However, in response to a personal name query, search engines return a long list of
search results containing Web pages about several namesakes. For example, when a user
submits a personal name such as ``William Cohen'' to the search engine, the returned results
contain more than one person named ``William Cohen.'' The results include a computer science
professor, politician, a surgeon, and others; these results are not into separate clusters
but are mixed together. Therefore, in order to disambiguate personal names
in Web search results, we develop more accurate clustering approaches.
[Selected publications]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Manabu Okumura: ``Personal Name Disambiguation in Web Search Results Using a Semi-Supervised Clustering Approach'' (in Japanese), Journal of Natural Language Processing, Association for Natural Language Processing (ANLP), Vol.16, No.5, pp.23-49, October 2009.
[pdf]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Manabu Okumura: ``Personal Name
Disambiguation in Web Search Results Based on a Semi-Supervised
Clustering Approach,''
The 10th International Conference on Asian
Digital Libraries (ICADL'07), Lecture Notes in Computer
Science (LNCS), Springer-Verlag, Vol.4822, pp.250-256, Hanoi, Vietnam, December 10-13,
2007. [pdf]
(4) Word Sense Disambiguation in Japanese Texts
I have developed several methods for supervised word sense disambiguation (WSD)
that use semi-supervised clustering based on the following ideas:
(a) sense-tagged word instances from various sources as supervised instances
in cases where word instances are grouped into clusters,
(b) features directly computed from word instances in the clusters that
are expected to be effective in supervised WSD since word instances
clustered around sense-tagged instances may have the same sense.
[Selected publications]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Manabu Okumura: ``Semi-supervised Clustering
for Word Instances and Its Effect on Word Sense Disambiguation,''
The 10th International Conference on Intelligent Text Processing
and Computational Linguistics (CICLing 2009), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Springer-Verlag,
Vol.5449, pp.266-279, Mexico City, Mexico, March 1-7, 2009. [pdf]
-
Kazunari Sugiyama and Manabu Okumura: ``Semi-Supervised Clustering for Word Examples'' (in Japanese), Information Processing Society of Japan (IPSJ),
SIG Technical Report 2008-NL (Natural Language)-184 (2), pp.7-12, Kyoto, Japan, March 2008. [pdf]
(5) Information Extraction from Biological Literature
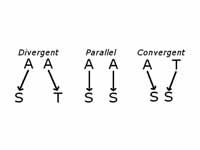
In the field of life science, the knowledge described in literature is
actively used with regard to protein-protein interactions. However, it is a quite
laborious task to identify protein-protein interactions from an enormous number of papers
and organize them as a knowledge system. Therefore, in order to support biologists' research,
I have developed several methods for extracting information on
protein-protein interactions from biological literature based on machine learning approaches.
[Selected publications]
- Kazunari Sugiyama, Kenji Hatano, Masatoshi Yoshikawa and Shunsuke Uemura: ``Extracting Information on Protein-Protein Interactions from Biological Literature Based on Machine Learning Approaches,'' The 14th International Conference on Genome Informatics (GIW2003), Genome Informatics, Vol.14, pp.699-700, Universal Academy Press, Yokohama, Japan, December 14-17, 2003. [pdf]




